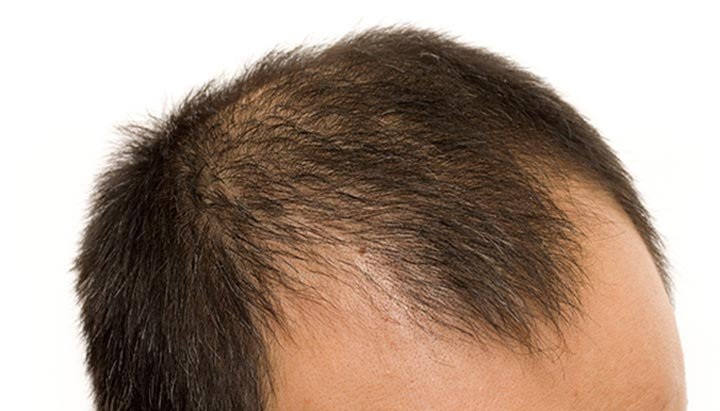
What is Alopecia?
Alopecia is partial or complete hair loss in areas where hair normally grows. There are several types of alopecia, including alopecia areata (patchy hair loss), alopecia totalis (total scalp hair loss), and alopecia universalis (complete loss of body hair). This condition can have various causes, including autoimmune disorders, genetics, stress, and certain medical treatments.
Alopecia can begin at any age. However, it most commonly begins in the late teens to early thirties. It is important to note that the onset of alopecia can vary from person to person, and there are different types of alopecia with different onset patterns. The condition affects both men and women, and the likelihood of developing it may be influenced by genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
Types of alopecia
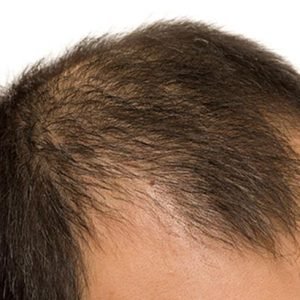
Androgenetic alopecia
Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this type of alopecia is the most common cause of hair loss. It is hereditary and can be influenced by hormones.

Alopecia areata
This type of alopecia causes hair to fall out in small patches.
It is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the hair follicles.
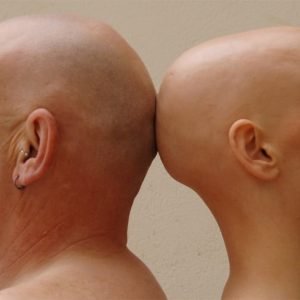
Alopecia totalis
Complete loss of hair on the scalp.

Alopecia universalis
This type of alopecia causes hair loss all over the body, including the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
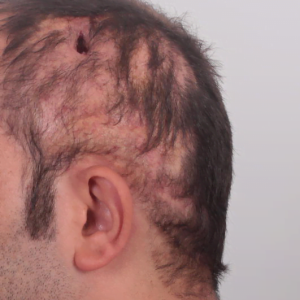
Scarring alopecia
Also known as cicatricial alopecia, this condition results in the destruction of hair follicles and hair loss due to inflammation.
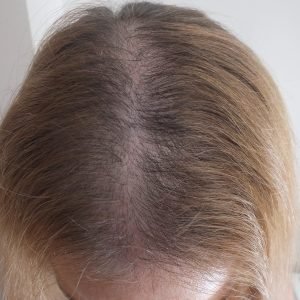
Anagen effluvium
Often caused by chemotherapy, this type of alopecia results in the sudden loss of actively growing hairs.

Telogen effluvium
This type of alopecia occurs when a significant amount of scalp hairs are shifted into the telogen (resting) phase, resulting in shedding and thinning of the hair.

Traction alopecia:
Traction alopecia is caused by repeated pulling on the hair, often due to certain hairstyles or hair treatments.
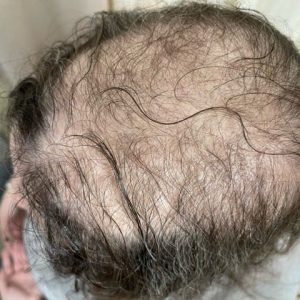
Trichotillomania
This is a psychological disorder where individuals have an irresistible urge to pull out their own hair, resulting in noticeable hair loss.
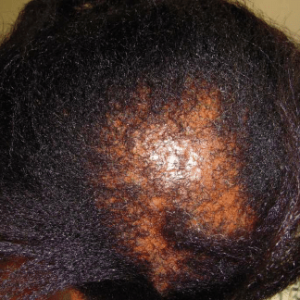
Chemical alopecia
Caused by exposure to certain chemicals, this type of alopecia can lead to hair loss and scalp irritation.
Symptoms of alopecia:
- Sudden loss of hair in round or oval patches on the scalp or other areas of the body
- Gradual thinning of hair on the scalp, leading to noticeable hair loss
- Full-body hair loss, known as alopecia universalis
- Itching or burning sensation in the affected areas
- Changes in the texture of the hair, such as becoming thinner or more fragile
Triggers of alopecia:
- Emotional stress or trauma
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes
- Autoimmune conditions
- Certain medications or treatments
- Infections or illnesses
- Excessive hairstyling or hair treatments
- Nutritional deficiencies
Causes of alopecia
Conventional medicine
According to conventional medicine, alopecia, or hair loss, can stem from a variety of factors. Genetics plays a significant role, with conditions like androgenetic alopecia often running in families. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, menopause, or due to thyroid disorders, can also contribute to hair loss. Certain medical conditions like autoimmune diseases (e.g., alopecia areata), scalp infections, and skin disorders can affect hair follicles and lead to hair loss. Medications used to treat various health conditions, emotional or physical stress, nutritional deficiencies, and excessive use of chemicals or harsh hair treatments can all play a part in causing alopecia.
Treatment methods for alopecia may include:
Minoxidil: this over-the-counter topical treatment is applied directly to the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
Corticosteroid injections:
Injections of corticosteroids into the scalp can help to reduce inflammation and stimulate hair growth.
Anthralin: this medication is applied to the scalp and is thought to alter the immune function in the skin, promoting hair regrowth.
Topical immunotherapy: this involves applying a chemical irritant to the scalp, which triggers an allergic reaction that may help hair to regrow.
Hair transplant surgery: in cases of advanced hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be an option to transplant hair follicles from one part of the scalp to balding areas. The effectiveness of these treatments can vary depending on the individual and the specific type of alopecia.
Functional medicine
Functional medicine takes a holistic approach to understanding and addressing the causes of alopecia. When it comes to alopecia, functional medicine practitioners may consider a variety of factors that could contribute to hair loss, including:
Nutritional deficiencies:
Assessing and addressing any deficiencies in key nutrients such as iron, zinc, biotin, and other vitamins and minerals that are essential for healthy hair growth.
Hormonal imbalances:
Investigating and balancing hormones such as thyroid hormones, sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen), and cortisol, as imbalances can contribute to alopecia.
Gut health: considering the health of the gut microbiome and its potential impact on inflammation and nutrient absorption, which can influence hair health.
Stress management:
Addressing chronic stress and its impact on the body, as stress can contribute to hair loss.
Immune function: investigating any underlying immune system imbalances or autoimmune conditions that may be linked to alopecia.
Chinese medicine
Alopecia is often addressed in Chinese medicine through a holistic approach that aims to get to the root cause of alopecia by rebalancing the body’s energy flow.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) views alopecia as a result of disrupted Qi (vital energy) and blood circulation, as well as imbalances in the internal organs.
Treatment may involve:
Acupuncture to stimulate energy flow and herbal remedies to nourish the blood and invigorate the Qi, and dietary/lifestyle adjustments to support overall health.
Additionally, TCM practitioners may use techniques such as cupping and scalp massage to improve circulation to the scalp and promote hair regrowth.
Impacts of alopecia on mental health, confidence and self esteem
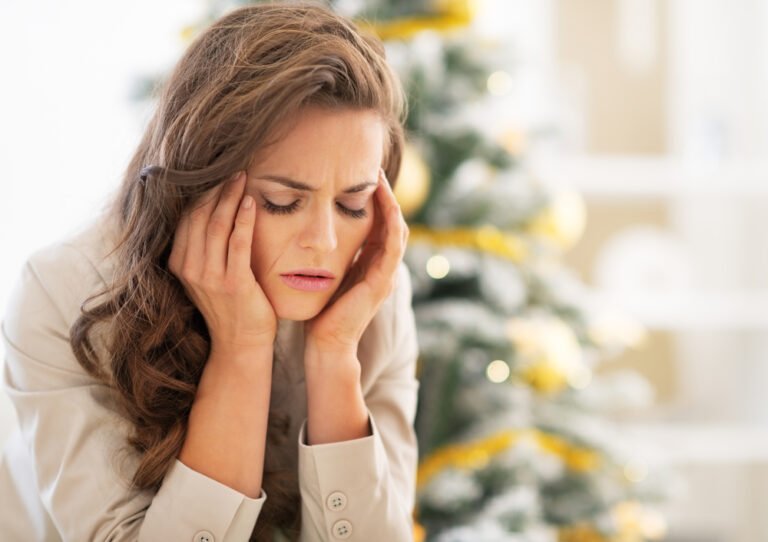

Alopecia can have a significant impact on confidence, self-esteem, and mental health. The experience of hair loss, especially in a society that often equates beauty with a full head of hair, can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and a decline in self-esteem.
Individuals with alopecia might struggle with their appearance and feel anxious about how others perceive them. This can lead to social withdrawal and feelings of isolation.
The psychological impact of alopecia can also contribute to conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Dealing with the emotional effects of hair loss, including the loss of identity and changes in self-image, can take a toll on mental well-being.

How does clinical hypnotherapy help to treat alopecia?

Hypnotherapy can be very effective in helping to treat skin conditions such as alopecia. The treatment can help to address the root cause of the condition through deep relaxation, suggestion, visualisation and other techniques. In this way unconscious psychological factors that could be contributing to or exacerbating flare-ups, such as stress, anxiety, self-esteem or other factors, have the potential to be resolved. As hypnotherapy is a treatment that is based on deep relaxation, therapy can also help break the vicious cycle of stress related hair loss.
Having alopecia can cause tremendous stress and frustration which can exacerbate the condition further, leading to even more hair loss. Clinical hypnotherapy can help promote a more positive self-image in such cases which can further reduce stress levels. Easy self-hypnosis tools given to you by your hypnotherapist can also increase your ability to manage stress in future. This can have an effect on long term treatment outcomes, potentially reducing or even eliminating stress related flare ups. As a treatment clinical hypnotherapy is relatively easy (you just sit back and relax) and the experience of deep relaxation during sessions is considered by many a pleasant, even ‘holiday-like’ experience.
Hypnotherapy can also have many positive side benefits. Chronic stress can wreak havoc on the entire body and its systems. Stress is known to alter the microbiome and can cause other health conditions. Chronic stress can also raise cortisol to unhealthy levels, disrupting important hormones and creating a toxic domino-like effect leading to inflammation and weakened immune system. Interrupting the stress cycle with clinical hypnotherapy can help break this pattern by giving the entire body a chance to heal and balance itself. In this way, clinical hypnotherapy can help to improve alopecia and have a positive effect on overall wellbeing at the same time. The therapy can also be used in conjunction with any other treatments that you may be undergoing.

How does clinical hypnotherapy help treat the psychological impacts of alopecia?

Hypnotherapy can offer several benefits for addressing the emotional and mental impacts of alopecia.
Stress reduction: hypnotherapy can help individuals manage the stress and anxiety often associated with alopecia, promoting a sense of calm and relaxation.
Improved self-image: by addressing negative thought patterns and boosting self-esteem, hypnotherapy can contribute to a more positive self-image for individuals with alopecia.
Coping strategies: hypnotherapy can empower individuals with alopecia by providing them with effective coping strategies to navigate the emotional challenges associated with the condition.
Enhanced emotional well-being: through techniques such as visualisation and guided imagery, hypnotherapy can support emotional well-being and assist in processing feelings related to alopecia.
Mind-body connection: hypnotherapy can help individuals foster a healthier mind-body connection, potentially improving overall mental wellness.

